Are You Stressed? | Symptoms & Warning Signs of Stress in 2023 You Shouldn’t Ignore

If there is one thing that unites us, it is stress. In today’s fast-paced environment, stress is quite prevalent, and your body and mind can pay a significant price if you do nothing about it. According to statistics from the American Psychological Association’s (APA) 2017, three out of every four Americans are stressed and suffered at least one stress symptom in their everyday life. Stress is a normal part of our life and can be caused by various factors, including work, relationships, finances, and health issues. However, the levels of stress may vary depending on various factors from person to person such as age, gender, occupation, personal circumstances and if left unchecked can lead to different health related problems.
Stress management training could help you in confronting stress in a healthier way. But first it is more important to understand the concept of stress and different aspects related to it.
Continue reading to learn about stress, its types and symptom’s.
What is stress?
Stress is any type of change that produces physical, emotional, cognitive and behavioral reactions in the human body. In reality, the human body is built to experience and respond to stress. Simply put, when you face changes and challenges also known as stressors in your surrounding, or feel pressured, frightened, or confront a situation that you do not think you can handle or control, your body then creates different types of physiological and psychological responses. That is called stress !

But stress is not always negative; it may be useful by keeping us alert, attentive, focused, and prepared to escape danger. It is a natural part of the human experience and can motivate us to take action and perform at our best. Stressful situations assist your body in adapting to new environments. For instance, If there is a difficult test coming up or we have a speech to give, a stress reaction may help your body function harder, get prepared, remain awake for longer period of time and give your best. However, when stress becomes chronic or overwhelming and persist without release or rest, it can have negative effects on our mental and physical health. Therefore, it is important to relieve and manage stress to prevent it from leading to more serious health problems.
What happens to the body during stress?
The autonomic nervous system of the body regulates your heart rate, respiration, visual changes, and other bodily functions. It also helps the body in dealing with stressful situations. and prepares it for inherent response to stress, known as the “fight-or-flight reaction”.
When an individual is under long-term (chronic) stress, the stress response (autonomic nervous system) is constantly activated, causing excessive wear and tear on the body. The symptoms of physical, emotional, cognitive and behavioral nature emerge.
Here are some of the changes that occur in the body during stress:
- Increased heart rate and blood pressure: When the body experiences stress, the heart rate increases , which raises blood pressure. This helps to supply more oxygen and nutrients to the muscles and brain.
- Activation of the adrenal glands: The adrenal glands release hormones such as adrenaline and cortisol in response to stress. These hormones help to mobilize the body’s energy resources and increase alertness.
- Increased respiration: Breathing becomes faster and shallower during stress, which helps to oxygenate the blood and deliver it to the muscles and brain.
- Constriction of blood vessels: Blood vessels in the skin and digestive system constrict during stress, which directs more blood to the muscles and brain.
- Increased muscle tension: Stress can cause muscles to tense up, which can lead to pain and discomfort.
These changes are part of the body’s natural response to stress. They help to prepare the body to deal with a threat or challenge.
Types of stress:
Depending on what happens in your life, stress can either be a short-term (acute) or a long-term (chronic) problem. A moderate degree of stress can often help us accomplish things and feel more focused. However, it may become a problem if it continues for an extended period of time. Stress may have an effect on all aspects of health and in some cases it may be referred to as ‘acute’ or ‘chronic’ by healthcare professionals.
Understanding the different types of stress can help individuals identify when they are experiencing stress and take active steps to manage it effectively.
ACUTE vs CHRONIC Stress
- Acute stress occurs from few minutes to few hours after an incident. It is quite intense but usually lasts for a small duration of time, generally less than a few weeks. It is a short-term response to a specific situation or event, such as a job interview or a near-miss car accident, a speech or it can occur after a traumatic or unexpected incident a sudden loss of someone or something, an attack, or a natural disaster. Acute stress is a normal part of life and can be helpful in motivating us to take action and perform at our best.
- Chronic stress persists for a long time or reappears. You could experience this if you are constantly under pressure. You may also experience chronic stress if your daily life is unpleasant, such as if you are a caregiver or live with limited resources, have a difficult work environment, financial problems, or a chronic health condition.
One of the most harmful part of stress is how rapidly it can overwhelm you. You start adapting to it. Moreover, it begins to feel natural, even regular. You’re not aware of how much it’s harming you, despite the fact that it’s taking a significant toll. That is why it is important to recognize the basic warning signs and symptoms of stress overload.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of any kind are broadly categorized into physical, emotional, cognitive, or behavioral changes that indicate the presence of an illness, injury, or other health condition. Symptoms can be a sign that something is wrong with the body, mind, or emotions, and they can range from mild to severe. Symptoms can include a wide variety of sensations, such as pain, fatigue, nausea, anxiety, confusion, memory loss, agitation, withdrawal, and others. It is important to pay attention to symptoms and seek medical attention if they persist or worsen over time, as they may indicate a serious underlying condition that requires prompt treatment.
Here are just a few of the many warning signs and symptoms of undue stress, which can come from anywhere.
- Physical symptoms
- Emotional symptoms
- Cognitive symptoms
- Behavioral symptoms
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it may be a sign that you are experiencing stress. It is important to take steps to manage stress to prevent it from leading to more serious health problems.
Physical symptoms:
Physical symptoms refer to any bodily sensations or changes that a person experiences. Hormones produced by our body in response to stressful conditions can have a variety of physical effects. These could include:

- Breathing difficulties – difficulty in breathing or shortness of breath.
- Blurred vision or aching eyes – unclear vision or pain/discomfort in the eyes.
- Fatigue – feeling tired or exhausted.
- Headaches and muscle pains – pain or discomfort in the head or muscles.
- High blood pressure and chest pains – elevated blood pressure and discomfort/pain in the chest area.
- Palpitations – the sensation of the heart racing, pounding, or fluttering.
- Heartburn or indigestion – burning sensation or discomfort in the chest or upper abdomen.
- Diarrhoea or constipation – frequent bowel movements or difficulty passing stool.
- Sickness, dizziness, or fainting – feeling nauseous, lightheaded, or losing consciousness.
- Weight gain or weight reduction that occurs suddenly – significant increase or decrease in body weight.
- The appearance of rashes or irritated skin – redness, itching, or inflammation on the skin.
- Sweating – excessive perspiration.
- Changes in your menstrual cycle or period – variations in the frequency or duration of menstrual cycles.
- Existing physical health issues are deteriorating – worsening of pre-existing health conditions.
- Immune system weakness – susceptibility to infections or illnesses.
- A painful jaw – discomfort or pain in the jaw.
- Hair is falling out – hair loss or thinning.
- Loss of sex drive – decreased interest in sexual activity.
- Frequent colds or flu – recurring episodes of cold or flu-like symptoms.
These physical effects might intensify if we are under a lot of stress. This can also happen if we are stressed for an extended amount of time. It is important to note that physical symptoms can have a wide range of causes, and it is often necessary to seek medical advice to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Emotional symptoms:
Emotional symptoms refer to any changes in a person’s emotional or mental state that may be related to their thoughts, feelings and beliefs. Stress can lead to emotional and mental symptoms like:
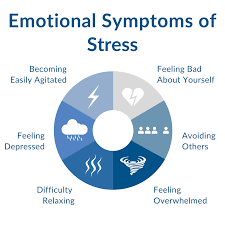
- Anxiety – a feeling of worry, unease, or apprehension.
- Irritated, furious, restless, or agitated – feeling annoyed, angry, or unable to relax.
- Overstretched or overloaded – feeling overwhelmed or burdened with responsibilities or tasks.
- Frightened or terrified – feeling scared or frightened.
- Unable to have fun – unable to enjoy or find pleasure in activities.
- Depressed – feeling sad, hopeless, or low in mood.
- Unwilling to engage in life – lacking motivation or interest in life activities.
- A feeling of lost sense of humor – feeling a lack of ability to find things funny or humorous.
- A feeling of doom – feeling a sense of impending danger or negative outcome.
- Concerned – feeling worried or concerned about something.
- Isolated or neglected – feeling alone or ignored by others.
- Current mental health issues are deteriorating – worsening of pre-existing mental health conditions.
- Eat to relax – using food as a coping mechanism to relieve stress or anxiety.
- Speaking quickly – talking fast or rapidly.
- Feeling out of control – feeling unable to control one’s emotions or actions.
- Lack of confidence – feeling unsure or insecure about oneself or one’s abilities.
- Lack of self-esteem – having a low opinion of oneself or feeling inadequate.
It is important to note that emotional symptoms can also have a wide range of causes, and seeking professional help from a mental health provider can be beneficial in managing and treating these symptoms.
Cognitive symptoms:
Cognitive symptoms refer to changes in a person’s thinking or mental processes
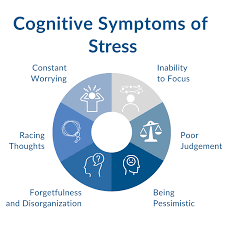
- Memory problems – difficulty in recalling or retaining information.
- Inability to concentrate – difficulty in focusing or paying attention.
- Poor judgment – making bad decisions or lacking good judgment.
- Seeing only the negative aspects – having a negative outlook or focusing only on negative aspects.
- Anxious or racing thoughts – experiencing persistent or racing thoughts related to anxiety or worry.
- Constant worrying – worrying excessively or persistently about various issues.
- Sleeping problems – experiencing difficulties falling asleep or staying asleep.
- Weird dreams – having strange or unusual dreams during sleep.
- Easily distracted – being easily sidetracked or losing focus due to distractions.
Cognitive symptoms can be caused by a wide range of conditions, including neurological disorders, brain injury, drug abuse, and mental health conditions. It is important to seek medical advice if cognitive symptoms persist or worsen over time.
Behavioral symptoms:
Behavioral symptoms refer to changes in a person’s actions or conduct that may be noticeable to others. These changes can include alterations in a person’s activity level, social interactions, and general behavior.
Often, people with chronic stress try to manage it with unhealthy behaviors, including:

- Smoking, using recreational drugs or drinking alcohol more than you usually would – increased use of substances that alter mood or behavior.
- Coffee or stimulants – consuming high amounts of substances that increase alertness or energy.
- Procrastinating or neglecting responsibilities – delaying or avoiding tasks or responsibilities.
- Gambling – engaging in excessive or problematic gambling behavior.
- Over-eating or developing an eating disorder – consuming excessive amounts of food or developing an unhealthy relationship with food.
- Participating compulsively in sex, shopping or internet browsing – engaging in excessive or problematic behaviors related to sex, shopping, or internet use.
- Snapping at people – responding with irritation or anger towards others.
- Experience sexual problems, such as losing interest in sex or being unable to enjoy sex – experiencing difficulties related to sexual desire or function.
- Restless, like you can’t sit still – feeling unable to sit still or rest.
- Cry or feel tearful – experiencing frequent or intense feelings of sadness or crying.
- Not exercising as much as you usually would, or exercise too much – engaging in either inadequate or excessive amounts of exercise.
- Social withdrawal – avoiding social interactions or becoming isolated.
- Rushing without doing anything – engaging in frenzied or hurried behavior without achieving anything.
- Nervous habits – engaging in repetitive or habitual behaviors due to nervousness or anxiety (e.g. nail biting, grinding teeth, clenching jaw, itchy skin).
- Prone to accidents – experiencing a higher than usual number of accidents or mishaps.
- Absenteeism – being absent from work or other obligations without a valid reason.
- Uncharacteristically lying – telling lies or being dishonest in ways that are unusual for the person.
Behavioral symptoms can be caused by a variety of factors, including mental health conditions, stress, trauma, and substance abuse. Seeking medical attention or professional help from a mental health provider can be beneficial in managing and treating these symptoms.
Help Is Available:
Sometimes, it is simpler for someone else to see signs of stress in you than it is for you to see them in yourself. Although it is simple to suggest that the symptoms will go away, but if they could not or they start to occur more frequently, then consult your doctor immediately.

Numerous stress-related symptoms might also be indicators of other health issues. Your doctor can assess your symptoms and find out any underlying medical issues. If stress is to blame, your physician may prescribe medication or even in worst conditions may suggest a therapist or counsellor to help you deal with stress more effectively. But eventually it become easier to deal with stress. Trust me !
Recommended Readings
- Diabetes prevention and treatment
- Top 10 Reasons why physical Fitness is Important for everyone.
- What if you have diabetes? Early signs & symptoms
- Mental Health is a Priority: 7 Powerful Trends in 2022
Follow us on Facebook for more.


0 Comments